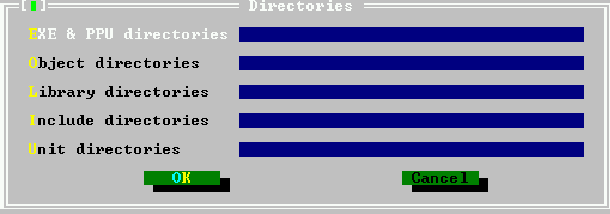
In the directory dialog, the directories can be specified where the compiler should look for units,
libraries, object files. It also says where the output files should be stored. Multiple directories
(except for the output directory) can be entered, separated by semicolons. The directories dialog is
shown in figure (6.21).
The following directories can be specified:
-
EXE & PPU directories
- Specifies where the compiled units and executables will go. (-FE
(see page 97) on the command line.)
-
Object directories
- Specifies where the compiler looks for external object files. (-Fo (see
page 98) on the command line.)
-
Library directories
- Specifies where the compiler (more exactly, the linker) looks for
external libraries. (-Fl (see page 97) on the command line.)
-
Include directories
- Specifies where the compiler will look for include files, included with
the {$i } directive. (-Fi (see page 97) or -I (see page 98) on the command line.)
-
Unit directories
- Specifies where the compiler will look for compiled units. The compiler
always looks first in the current directory, and also in some standard directories. (-Fu
(see page 98) on the command line.)